Commercial Laundries

Laundries use large volumes of water with potential for significant water efficiency and cost savings!
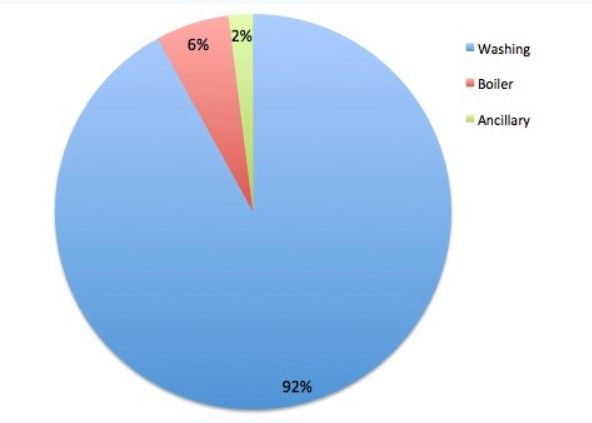
- Where does the water in a Non-Residential Laundry go? A water balance allows the total water use within an organisation to be contextualised, including areas that might otherwise be overlooked.
- In a typical Non-Residential Laundry, the washing process represents 90-92% of water used, steam generation accounts for 5-8% and ancillary water use makes up 2-3%. It is conceivable, then, that the greatest potential savings will be found within the washing process. However, simple and cost effective savings can be also found in steam system design and maintenance.
Typical Non-Residential Laundry water balance
In the case of Non-Residential Laundry, it would be easy to overlook the major contribution from steam generation within a facility's water consumption. Water conservation initiatives targeting ancillary water use may not initially appear to deliver significant savings. However, with ancillary water use proportional to the large volumes used in the washing process, it can in fact be as much as 3,000kL per year.
Benchmarks and efficiency ratings – what might you expect?
Several benchmarking studies have worked to establish ‘good practice’ guidelines within the Non-Residential Laundries industry, resulting in standardised benchmarks for washer-extractors and continuous batch washers.
For washer-extractors, a range of 17-22 L/kg is considered good performance without the application of water conservation techniques.
For continuous batch washers, the established benchmark is 7.5-12L/kg.
When integrated with rinse water collection and reuse, washer extractor consumption can drop to 12-15 L/kg.
Applying recycling systems to continuous batch washers can further improve water efficiency by 40-80% (system dependent) resulting in a performance range of 1.5 to 4.5 L/kg of linen processed.
The following statistics provide a guide to water efficiency within each of the laundry segments. They are based on whole laundry performance and include the effects of specific technology and rewash rates.